Description
Description
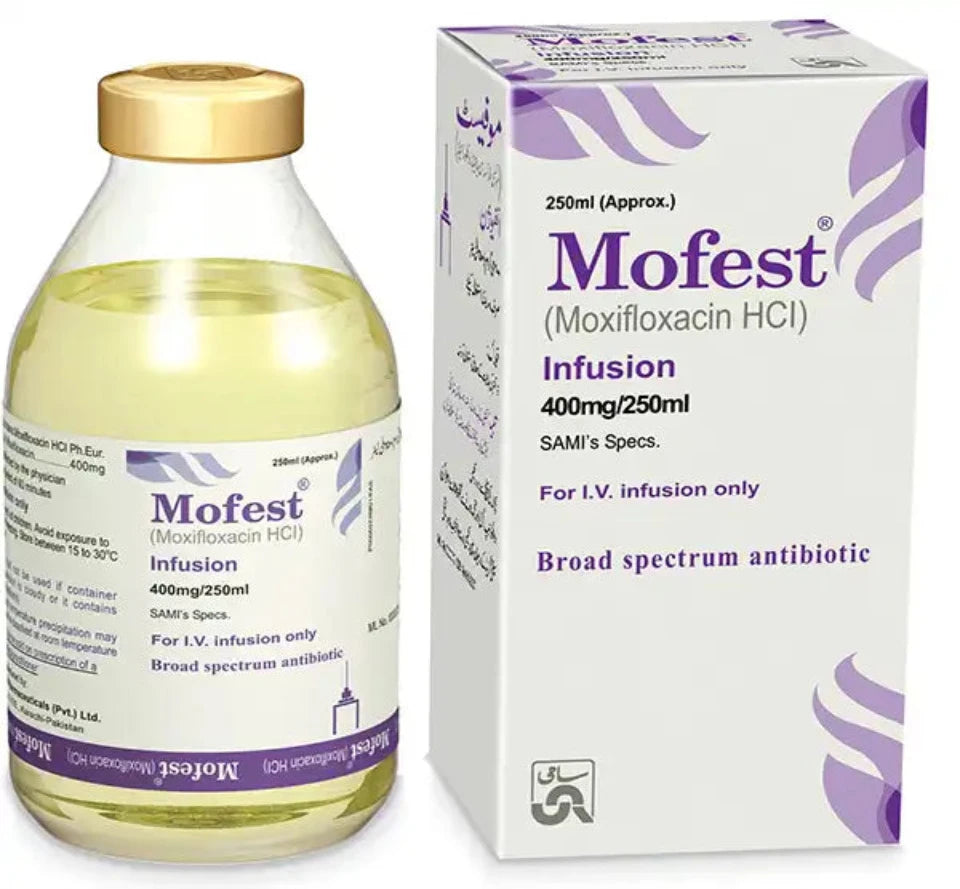
SPECIFICATION
400Mg 1 Vialx250ml
Generics
Moxifloxacin HCl
About
Moxifloxacin has in vitro activity against a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative microorganisms. The bactericidal action of moxifloxacin results from inhibition of the topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase) and topoisomerase IV required for bacterial DNA replication, transcription, repair, and recombination. It appears that the C8-methoxy moiety contributes to enhanced activity and lower selection of resistant mutants of Gram-positive bacteria compared to the C8-H moiety. The presence of the bulky bicycloamine substituent at the C 7 position prevents active efflux, associated with the NorA or pmrA genes seen in certain Gram-positive bacteria.
Indication
It is indicated for the treatment of adults (> 18 years of age) with infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in the conditions listed below: Acute Bacterial Sinusitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, or Moraxella catarrhalis. Acute Bacterial Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus, or Moraxella catarrhalis.Community Acquired Pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Side Effects
BODY AS A WHOLE: Abdominal pain, headache, asthenia, injection site reaction (including phlebitis), malaise, moniliasis, pain, allergic reaction CARDIOVASCULAR: Tachycardia, palpitation, vasodilation, QT interval prolonged DIGESTIVE: Vomiting, abnormal liver function test, dyspepsia, dry mouth, flatulence, oral moniliasis, constipation, GGTP increased, anorexia, stomatitis, glossitis HEMIC AND LYMPHATIC: Leukopenia, eosinophilia, prothrombin decrease (prothrombin time prolonged/International Normalized Ratio (INR) increased), thrombocythemia METABOLIC AND NUTRITIONAL: Lactic dehydrogenase increased, amylase increased MUSCULOSKELETAL: Arthralgia, myalgia NERVOUS SYSTEM: Insomnia, nervousness, vertigo, somnolence, anxiety, tremor SKIN/APPENDAGES: Rash (maculopapular, purpuric, pustular), pruritus, sweating, urticaria SPECIAL SENSES: Taste perversion.
Drug Interactions
Drugs that prolong the QT interval including antiarrhythmics , antipsychotics , neuroleptics , TCADS , antimicrobials , antihistamins , cisapride. Corticosteroids , hypokalaemic agents , anticoagulants, Antacids , didanosine , sucralfate , charcoal , iron or zinc supplements.
When not to Use
Moxifloxacin is contraindicated in persons with a history of hypersensitivity to moxifloxacin or any member of the quinolone class of antimicrobial agents.
Precaution
Quinolones may cause central nervous system (CNS) events, including: nervousness, agitation, insomnia, anxiety, nightmares or paranoia.